Diamond & CBN Grindstones Selection Guide Diamond & CBN Grindstones for Flat Surfaces Selection Method (Reference)
Features of CBN
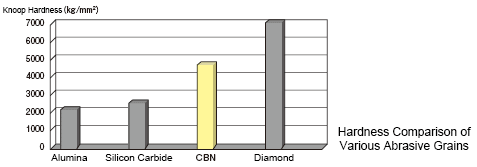
Hardness of CBN
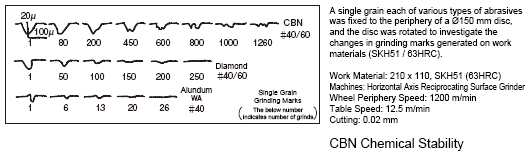
Stability of CBN
Diamond & CBN Wheel Periphery Speeds (Reference)
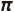 (Pi) x Wheel Axis Rotations ÷ 1000
(Pi) x Wheel Axis Rotations ÷ 1000Use the wheel periphery speeds shown below as guidelines.
| Abrasive Grain | Diamond | CBN | ||
| Grinding Method | Wet Grinding | Dry Grinding | Wet Grinding | Dry Grinding |
| Periphery Speed (m/min) | 1,200 ~ 1,800 | 700 ~ 1,200 | 1,500 ~ 2,400 | 1,200 ~ 1,500 |
Diamond & CBN Wheel Cutting Depths (Reference)
| Particle Size | #140 | #170 | #220 | #325 | #400 ~ |
| Cutting Depth (mm) | Within 0.025 | Within 0.02 | Within 0.015 | Within 0.010 | Within 0.005 |
Relation of Particle Size and Surface Roughness of Diamond & CBN Grindstones (Reference)
| Particle Size | Surface Roughness (Ry) |
| #140 | Approx. 3 μm |
| #400 | Approx. 1 μm |
| #1000 | Approx. 0.4 μm |
■ For CBN when grinding high-speed steel work materials
| Particle Size | Surface Roughness (Ry) |
| #140 | Approx. 3 μm |
| #400 | Approx. 2 μm |
| #1000 | Approx. 1 μm |
Supplementary Data: CBN Particle Size (#), Bonds, Binding Degree & Concentration
| What is Particle Size (#)? | What are Bonds? | What is Binding Degree? | What is Concentration? |
| Particle size indicates the size of the diamond and CBN grains on the wheel. | Bonds keep the diamond and CBN abrasive grain on the wheel, and are made of resin and other types of fillers. | Binding degree indicates how strongly the diamond and CBN grains stick to the wheel. | Concentration represents the amount and thickness of diamond and CBN grains on the wheel. |
| The particle size "#" is also known as the "mesh size". For instance, #140 (or 140 mesh) indicates an average particle size of 105 μm, and #400 (or 400 mesh) indicates an average particle size of 37 μm. Check the "Particle Size Selection Table (reference)" below for more information on particle sizes. | Codes for all resin bonds in the JIS system start with the letter "B". After this letter, manufacturers enter their own codes for each of their products. Check the "Diamond & CBN Wheel Selection Table (reference)" below for more information on selection methods by work material type and grinding methods. | Considering the letter "N" as the median value, it is typical to select "L" when soft binding and a sharp wheel are required, and conversely "P" when hard binding and a long wheel life are required. | A concentration of 100 stands for a proportional grain volume of 25% in the grain layer. The higher the concentration, the more grains in the layer, which in turn makes the product more expensive. Check the "Diamond & CBN Concentration Selection Table (reference)" below to find out CBN grain volumes in a layer block of 1 cm3. |
 |
Check the "Diamond & CBN Wheel Selection Table (reference)" below |  |
 |
Diamond & CBN Wheel Selection Table (reference)
| Work Material | Grinding Method | Abrasive Grain | Particle Size | Bonds | Binding Degree |
| Carbide | Rough / Wet | Diamond | #140 | BW | P |
| Rough / Dry | #140 | BWD | P | ||
| Finish / Wet | #400 | BW | N | ||
| Finish / Dry | #400 | BWD | N | ||
| Mirror / Wet | #1200 | BW | L | ||
| Simultaneous grinding of carbide / steel | Rough / Wet | Diamond | #140 | BD | P |
| Rough / Dry | #140 | BDD | P | ||
| Finish / Wet | #400 | BD | N | ||
| Finish / Dry | #400 | BDD | N | ||
| Steel (Alloy tool steel, quenched high-speed steel, 400 series quenched stainless steel) |
Rough / Wet | CBN | #140 | BS | P |
| Rough / Dry | #140 | BSD | P | ||
| Finish / Wet | #400 | BS | N | ||
| Finish / Dry | #400 | BSD | N | ||
| Cast Iron | Rough / Wet (water base) | Diamond | #140 | BW | P |
| Rough / Wet (oil base) | CBN | #140 | BS | P | |
| Finish / Wet (water base) | Diamond | #400 | BW | N | |
| Finish / Wet (oil base) | CBN | #400 | BS | N |
 Essentially for high hardness steel, not recommended for mild steel and pre-hardened steel.
Essentially for high hardness steel, not recommended for mild steel and pre-hardened steel. Not recommended for 300 series or stainless steel.
Not recommended for 300 series or stainless steel. Durability will fall drastically when grinding steel with hardness of 50 HRC or less. Use for grinding especially high hardness steel.
Durability will fall drastically when grinding steel with hardness of 50 HRC or less. Use for grinding especially high hardness steel. Not recommended for wet grinding for mirror finishes.
Not recommended for wet grinding for mirror finishes. Selection between water and oil bases may vary for wet types.
Selection between water and oil bases may vary for wet types.Diamond & CBN Wheel Particle Size Selection Table (reference)
| Diamond & CBN Display Particle Size |
JIS Particle Size | Average Particle Size (μm) |
| #140 | #140 / #170 | 105 |
| #170 | #170 / #200 | 88 |
| #200 | #200 / #230 | 74 |
| #325 | #325 / #400 | 44 |
| #400 | - | 37 |
| #600 | - | 30 |
| #800 | - | 20 |
| #1000 | - | 15 |
| #1200 | - | 13 |
Diamond & CBN Concentration Selection Table (reference)
| Concentration | Abrasive Grain Ratio (Volume) |
Used Carats (ct / cm3) |
| 75 | 18.8% | 3.3 |
| 100 | 25% | 4.4 |
* 1 carat = 0.2 g
 A larger grain volume may not necessarily lead to better grinding performance. Depending on work conditions, poor grinding results may occur even with larger grain volumes.
A larger grain volume may not necessarily lead to better grinding performance. Depending on work conditions, poor grinding results may occur even with larger grain volumes.

